Meiosis I Stages Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Biology Diagrams Meiosis is the special type of recombinative and reductive cell division occurring only in the generation of the gametes or germ cells (oocyte and spermatozoa). For recombination, meiosis requires that homologous chromosomes are properly paired and aligned by the induction of DNA double-strand breaks by the enzyme SPO11 during the prophase of

The daughter cells produced by a reduction division are not identical to the parent cells, as is the case in mitosis. The diagram below provides an overview of the series of steps, or phases, that are involved in a single meiotic division. Meiosis occurs only in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cell division occurs via binary fission. The chromosomes in each sperm or egg are a random mix from the maternal set and paternal set of the original cell. Because each of the 23 pairs of chromosomes sort independently of the other 22 pairs, one person can produce more than 8 million different kinds of eggs or sperm. By means of sexual intercourse, a sperm cell carrying one 23 chromosome set from the father reaches and fuses with an
Definition, Process, Stages, & Diagram Biology Diagrams
(genetics) cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; the nucleus divides into four nuclei each containing half the chromosome number (leading to gametes in animals and spores in plants).reduction division The first cell division in meiosis, the process by which germ cells are formed.

Definition of Meiosis. Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms. It consists of two sequential divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, and leads to the formation of four genetically diverse haploid cells from one diploid cell. 2. Importance of Reduction Division A. Maintaining Chromosome Number
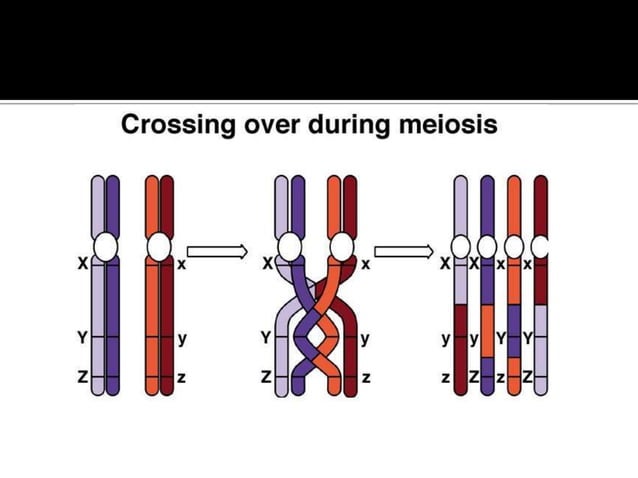
BioNinja Biology Diagrams
3. Again correct in the "Results of Meiosis I" statement. 4. First diagram of the whole process is mislabeled at the end of Cytokinesis 1 and the Prophase II picture. In the "script" is correctly states Meiosis is reduction/division, Meiosis I REDUCES the number of chromosomes, then Meiosis II DIVIDES them.

Meiotic cell division is called by reduction division because the produced cells contain half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell. Importance of Meiosis. Maintains chromosome number across generations. Generates genetic diversity, which is essential for evolution and adaptation. Allows sexual reproduction and formation of gametes.
